This is like setting a timeframe to see how quickly you turn your inventory into sales. Due to this, you should be comparing value among their same sector peer companies. When you look at technology, automobile, and furniture sectors, these companies can hold inventory for long durations. As you know, eggs go bad, so these Certified Public Accountant companies need to move inventory as quickly as possible.

Your quick guide to understanding B2B inventory management
- Looking at the changes in DSI over time is another way to get great context on the formula.
- If the inventory turnover ratio is high, the company handles the inventory well, and the stock is not outdated, which naturally means lower holding costs.
- Inventory turnover, on the other hand, looks at how often the inventory is sold and replaced during a period.
- A low DSI value generally means that a company is balancing sales with inventory well.
- The denominator (Cost of Sales / Number of Days) represents the average per day cost being spent by the company for manufacturing a salable product.
- If you know how many sales you make per year, you might wonder why it matters how long each piece of inventory takes to sell.
Generally, low DSI values are preferred since it indicates the smart conversion of inventories. Ideally, a good DSI is 30–60 days (depending on the entity’s size and industry). A rising DSI inventory ratio could indicate either (or both) falling demand for a company’s products or a poor reading by management of future demand (leading to inventory write downs). To decrease the number of days it takes to sell your stock, you can work to increase your rate of sales.
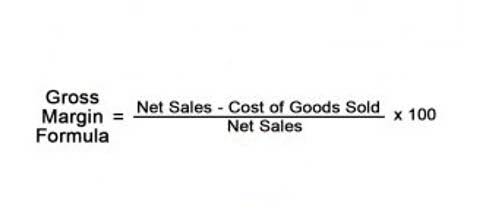
Days sales in inventory formula
For seasonal businesses, DSI needs a tailored approach to account for fluctuations in demand. These businesses should calculate DSI for their peak and off-peak seasons separately to gain accurate insights. Understanding these seasonal variances helps in better inventory planning and ensures that the business is not caught off-guard during high-demand periods. When you use both dsi accounting these measures, you get a full picture of how well a business is handling its inventory. This helps in making sure the inventory is managed efficiently, balancing how quickly items are sold with how often new stock is brought in. Often, businesses look at a full year, which is 365 days, but you can choose a shorter period if it suits your business better.
Examples of Bad DSI Trends
- A financial ratio called inventory turnover indicates how frequently a business rotates its stock in relation to its cost of goods sold (COGS) during a specific time frame.
- While this can give you an indication of how efficiently your business is operating, it’s important to remember that different industries will have different benchmarks.
- Yes, if a company ends up selling more goods than the inventory it has, the turnover can become negative.
- By monitoring these trends, businesses can adjust procurement and production schedules to maintain optimal inventory levels.
A low DSI suggests that a firm is able to efficiently convert its inventories into sales. This is considered to be beneficial to a company’s margins and bottom line, and so a lower DSI is preferred to a higher one. A very low DSI, however, can indicate that a company does not have enough inventory stock to meet demand, which could be viewed as suboptimal. While inventory value is available on the balance sheet of the company, the COGS value can be sourced from the annual financial statement. Care should be taken to include the sum total of all the categories of inventory which includes finished goods, work in progress, raw materials, and progress payments. For instance, a designer sofa may take longer to sell than a book, but the profit margins will be higher, which could compensate for the carrying costs involved in storing the item.
- DSI should be calculated regularly, ideally at the end of each accounting period, which could be monthly, quarterly, or annually.
- The calculation of DSI value is important to companies and their stakeholders since it throws insight into the efficiency of inventory management and the company’s performance.
- This is like setting a timeframe to see how quickly you turn your inventory into sales.
- DSI is calculated based on the average value of the inventory and cost of goods sold during a given period or as of a particular date.
- DSI is also known as the average age of inventory, days inventory outstanding (DIO), days in inventory (DII), days sales in inventory, or days inventory and is interpreted in multiple ways.
Ways to optimize days sales in inventory

One metric that can help you gain valuable insights into your inventory management is the Days Sales of Inventory (DSI). In this blog post, we will explore the definition, formula, and importance of DSI, shedding light on how it can law firm chart of accounts enhance your financial decision-making process. By continuously monitoring DSI and other related KPIs, inventory management software provides a dynamic view of turnover trends. This enables companies to spot patterns or shifts in product movement that may indicate emerging market trends or internal process inefficiencies.
